External cephalic version ECV
Breech presentation occurs in 3-4 % of term deliveries, It is more common in preterm and nulliparous women. And It is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities.
In many countries planned vaginal breech birth remains rare and attempts to prevent breech presentation remain important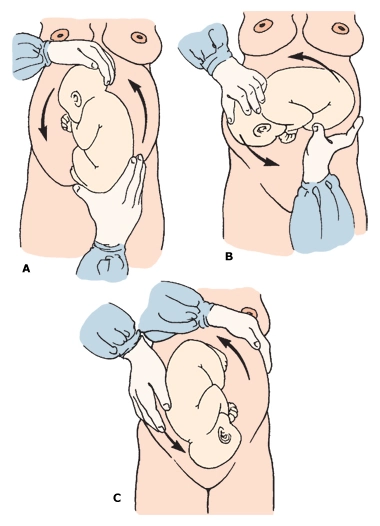
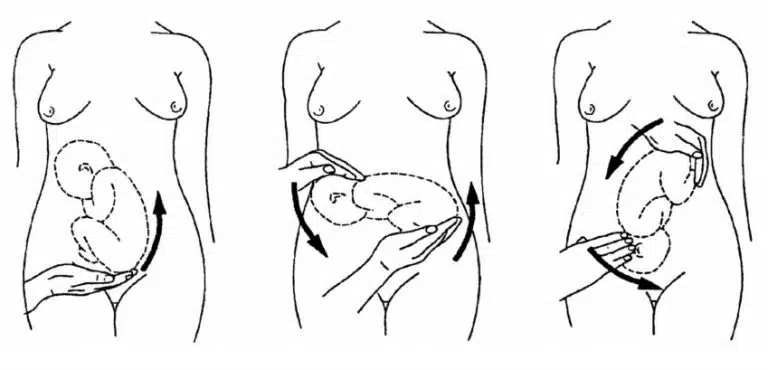
External cephalic version is a manual procedure that is used to turn a baby from a breech or side-lying position to a head-down position in the womb in order to enable vaginal delivery .
During the procedure, the healthcare provider places their hands on the outside of the belly and attempts to rotate the baby. The baby's heart rate is monitored to check for any problems.
-The success rate of ECV is 50 % ,Success levels are greater for multiparous women (60 %) than for nulliparous women (40%)
After successful ECV 3% of babies revert to breech
Labor after ECV is associated with a slightly increase risk of cesarean sections and instrumental delivery when compared with spontaneous cephalic presentation due to obstructed labor and fetal distress
ECV at term decreases non-cephalic presentation at delivery and decreases the rate of cesarean sections
The risk of cesarean section may be greater with a shorter ECV to labor interval
TIMING of ECV
In nulliparous women it is offered from 36 weeks
In multiparous women from 37 weeks
No upper gestational limit for when ECV can be offered
Contraindications to ECV:
- Where an absolute reason for CS already exists
- Placental abruption
- Placenta previa
- Recent vaginal bleeding ( less than 1 week )
- Severe PET
- Abnormal doppler or CTG
- Twins
- Rhesus isoimmunization
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
Complications of ECV
- Placental abruption
- Fetal bradycardia
- Fetomaternal hemorrhage
- Emergency CS due to abnormal CTG or vaginal bleeding or unexplained abdominal pain
Who should perform ECV
It should only be performed by a trained practitioner
Predictors for successful ECV
- Multiparity
- Non engagement of the breech
- Palpable fetal head
- Maternal weight less than 65 kg
- Posterior placental location
- Complete breech presentation
- Amniotic fluid index more than 10
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
