Laparoscopy Surgery - Gynecological Laparoscopy
What is Laparoscopy (Key Hole Surgery)?
Laparoscopy is usually done under general anesthesia although it could be done using local anesthesia.
The laparoscopy is a procedure done for diagnostic or operative purposes, and in many cases is done as a combined diagnostic and operative procedure where the cause is found and dealt with at the same time .
It is done by inserting a small telescope which has a light source and is attached to a camera, and a monitor used to visualize the internal organs.
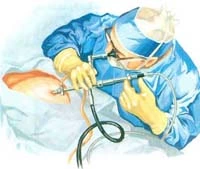
The laparoscopy ( key hole surgery ) has an advantage over conventional operations in that the operation is less painful and with a shorter hospital stay for the patient in addition to better cosmetic results and ability to resume normal activities in a shorter time after the operation.
A small cut is made under or through the navel where a thin needle is inserted into the abdominal cavity and is used to insert gas (CO2). The abdomen is insufflated to a certain degree of pressure, and then a trocar is introduced through the small cut, and the telescope inserted through it. The camera is then attached to the telescope to enable the internal organs to be viewed on a monitor. Smaller-sized trocars are then inserted into the lower part of the abdomen & on either side (could be three in total). Instruments could then be introduced into the abdomen through the trocars, enabling the operator to perform his procedure.
Recovery after Laparoscopy
In the recovery room, the attending nurse will observe the patient until she is conscious, and then the patient will be returned to her room, if she is discharged on the same day, she is not allowed to drive.
As a result of the anesthetic the patient might feel tired and dizzy, which is normal. Some feel shoulder pain for the first 24 hours after the operation.
Minor complications could result from the operation manifesting as redness at the incisions sites or leakage of fluid from the cut sites or a small degree of fever. All of these complications are rare and easily controlled by the attending doctor.
Indications and Uses of Gynecological Laparoscopy
Gynecologists use laparoscopy to treat a variety of female health problems. General surgeons also now use laparoscopy to perform surgeries such as appendectomies and removal of the gall bladder (cholecystectomy). Indications for gynecological laparoscopy include the following:
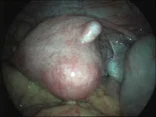
Ovarian cysts and tumours.
An enlarged ovary could be due to the cystic area within the ovary or due to solid mass.
The surgeon could differentiate between them and remove any cyst or tumour through the laparoscope or take a biopsy if cancer is suspected, or remove the whole ovary if needed.
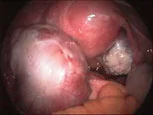
Removal of fibroids (Myomectomy).or destroying them (Myolysis )
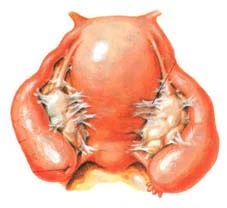
Fibroids are benign tumours (growth) which arise from the wall of the uterus. Around 20% or more of women over 35 years old have fibroids. Women might suffer from painful periods or heavier periods. In pregnancy, it could lead to complications e.g. premature labour.
Fibroids
Infertility, Lysis of adhesions.
Adhesions are a major cause of infertility. This usually happens as a result of previous surgery or pelvic infection. By operative laparoscopy, the adhesions are cut and there is a fewer chance of them recurring than if the same operation is done by opening the abdomen in the conventional technique.
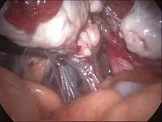
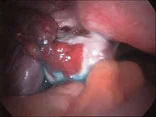
Infertility, checking the condition and patency of the Fallopian tubes
The Fallopian tubes are checked at the time of laparoscopy, their condition and patency are noted, die is injected through the neck of the uterus, and if the tubes are patent, free spill is noted.
Reproductive or tubal surgery
Repairing damaged Fallopian tubes.
In this condition part of the lining of the uterus (endometrium) implants outside of the uterus in the pelvis and abdomen, e.g. on the ovary, and the intestine. On the ovary it could form a collection of blood in a cystic cavity where it is called a chocolate cyst.
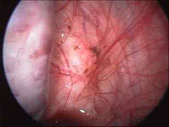
This condition leads to adhesions, cause pain during and before periods, painful intercourse (dyspareunia), painful defecation, or painful urination.
This condition could lead to infertility, and diagnosis is usually by laparoscopy and if adhesions are found they are dealt with promptly.
Intraperitoneal Hemorrhage.
In cases of intraperitoneal hemorrhage where the cause is unknown, laparoscopy is used to find the source. Once found it can be dealt with. In some cases this could be the result of pregnancy in the Fallopian tube [ectopic pregnancy], and it is dealt with using the laparoscopy equipment.
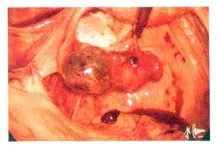
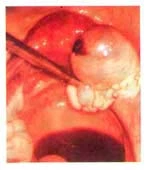
This condition affects one in five women as a result of disorder in the function of the ovary where many follicles are formed (much more than normal), but they stay small and don’t mature.
It is usually diagnosed by ultrasound and treated by medicines. Surgery is only resorted to in resistant cases where multiple ovarian drilling is done using the laparoscope.
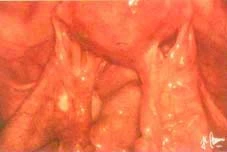
Pelvic infection (Pelvic Inflammatory disease ):
This is diagnosed using the laparoscopy, especially in chronic cases where the cause of pelvic pain is unknown, A sample is taken and sent for bacteriological culture, and the appropriate antibiotics are given.
Egg collection for assisted reproduction:
This is done in some case, e.g gamete intrafallopian transfer, or in some cases of in vitro fertilization where the ovaries are high up in the abdomen, and the eggs could not be collected using the vaginal ultrasound.
Sterilization ( laparoscopic sterilization)
Couples who don’t want to have any more children could have this procedure done where the women undergo laparoscopic sterilization (the tubes are closed using clips or rings or cauterized).
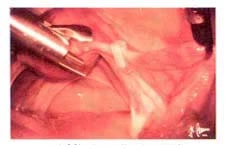
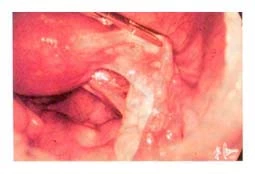
Severe period pain
Diagnosis and treatment of some uterine anomalies.
Pelvic floor and vaginal prolapse
Urinary incontinence
Some reproductive cancer
Evaluation and removal of pelvic lymph nodes.
Where it is indicated to remove the uterus, this procedure is done either completely using the laparoscopy or through the vagina (Laparoscopic assisted vaginal hysterectomy).
Dr Najeeb Layyous F.R.C.O.G
Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist and Infertility Specialist







 Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
 Chinese Gender Predictor
Chinese Gender Predictor
 Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation Calculator
 IVF Due Date Calculator
IVF Due Date Calculator
